Definition
Data Structures is a data organization, management and storage format that enables efficient access and modification. (Access-Insertion-Deletion-Search)
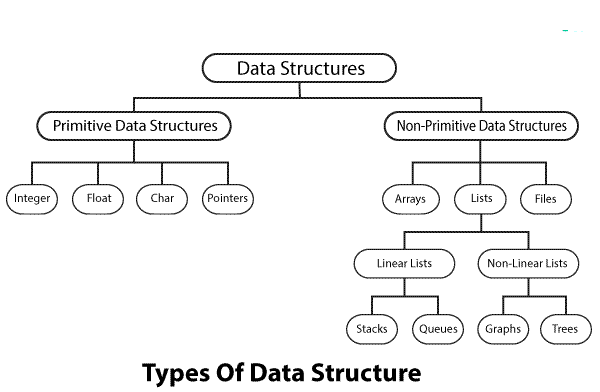
Types of Data Structures
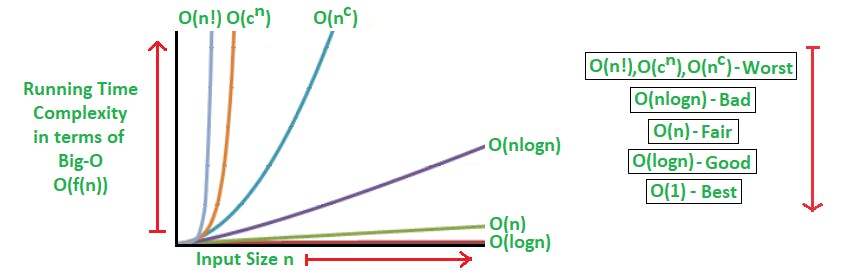
Complexity
The time complexity is the computational complexity that describes the amount of computer time it takes to run an algorithm.
for example if we want to search for an element in an Array and if we loop on each element in the array we might find the element in the first index of the Array (best case) or we will find it in the middle of the Array (average case) or it might be the last element of the Array (worst case).
- Best case (omega notation)
- average case (theta notation)
- worst case (Big O notation)
we will consider the worst case because it is more important.
Time complexity Calculation
The operations (*, /, %, ^, +, -, ++, --, +=, -=, /=, *=) and the condition statements (if, else, if else) they take constant time O(1).
if we want to get the sum of numbers from 1 to n we can't do that by a simple loop
for(int i =1; i <=n;i++){
sum = sum+i;
}
the previous simple loop will take n statement to complete, so the complexity of the loop is O(n).
- If we have a nested loop
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
for(j=0;j<n;j++){
//statement;
}
}
the previous code will take O(n^2).
- if we have increment in the loop index
for(i=0;i<n;i=2*i){
//statement;
}
the complexity of the previous code will be O(log n). note the base of the log in the previous code is 2.
- Another example for calculating time complexity
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
for(j=0;j<n;j++){
for(k=0;i<n;k=2*k){
//statement;
}
}
}
the complexity of the previous code will be O(n^2 log n). note the base of the log in the previous code is 2.
- Another example for calculating time complexity
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
for(j=0;j<n;j=2*j){
for(k=0;i<n;k=2*k){
//statement;
}
}
}
the complexity of the previous code will be = n/2 * log n * log n O(n log n^2). note the base of the log in the previous code is 2.
Since an algorithm's running time may vary among different inputs of the same size, so we should consider the worst-case time complexity as a one of the most important thing in learning Data Structures and Algorithms.
